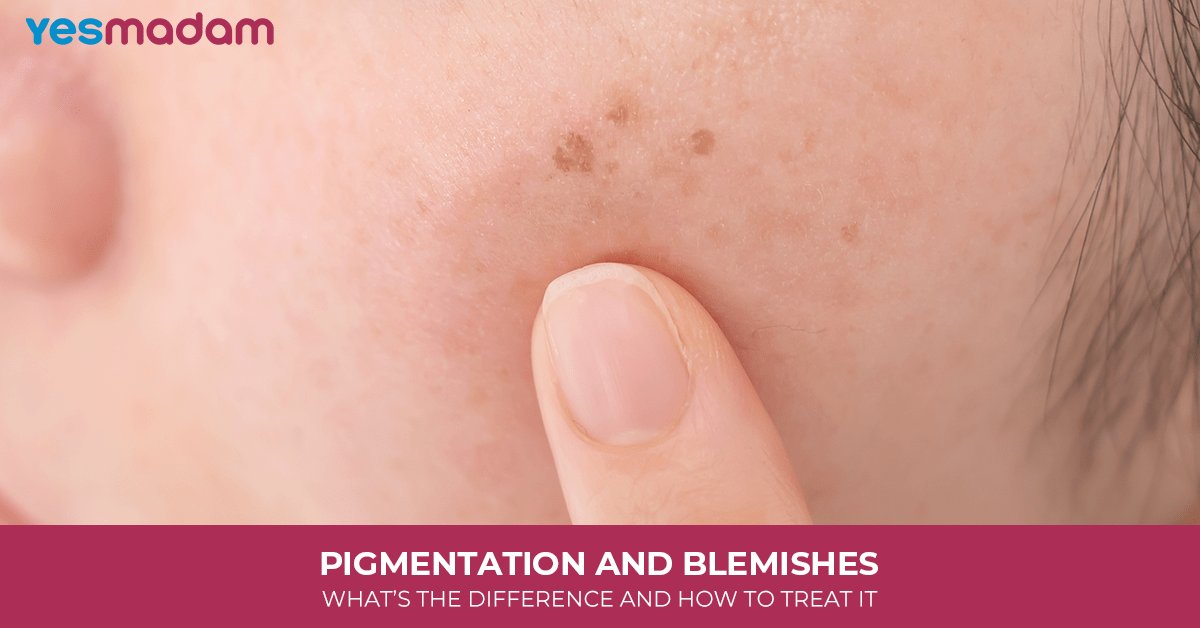
Pigmentation And Blemishes: What’s The Difference And How To Treat It
For most people, the daily mirror check is a practice as ingrained as brushing our teeth. It’s all smooth sailing until you notice uneven tone, marks, or spots that were not there the last time you checked -at least as far back as your memory goes.
These common concerns, like dark spots, pigmentation, or blemishes, may look similar, but they are different in multiple aspects.
This is where the blog steps in to help you understand the difference between pigmentation and blemishes. And also to some extent between pigmentation and dark spots.
This blog will help you understand what blemishes, pigmentation are. How are they different from dark spots, and what is the best treatment for blemishes and pigmentation on the face to get clear and even-toned skin?
Table of Contents
What Are Blemishes?

Blemishes are any spot, imperfection, or mark on the skin. These are often visible as marks or lesions on your skin’s surface. Blemishes also differ in colour, with some being inflamed and red, while others are dark or lighter.
Causes of Blemishes
- Acne: Stems from hormonal changes, excess oil production, and the presence of acne-causing bacteria on the skin.
- Clogged pores: When pores get clogged with oil, dirt, or dead skin cells, it may cause the development of blackheads, whiteheads, or pimples.
- Scars: Left behind by skin injuries, acne, and other skin problems.
Common Types Of Skin Blemishes
Acne: Problems like blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, or even cystic acne due to excess oil production and clogged pores.
- Dark spots: Also called post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), it is a type of discoloration left behind once the scar is healed.
- Freckles and sun spots: Small, dark brown spots due to extreme sun exposure or genetics.
- Skin irritations: Blemishes that are mostly caused due to rashes, allergies, or even bacterial infections.
What is Pigmentation?

Pigmentation is a change in skin colour caused due to uneven melanin production. It looks like dark patches or flat spots on the skin.
Causes of Pigmentation
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy can lead to the development of dark spots.
- Sun exposure: UV radiation stimulates melanin production. This causes the formation of sun spots, also called age spots.
- Ageing: With ageing, the skin’s natural ability to repair and regenerate on its own may diminish. This can cause accumulation of melanin in certain parts, causing age-related dark spots.
- Hyperpigmentation: Dark spots due to injury or inflammation, such as acne, for example.
Types Of Skin Pigmentation
- Melasma: brownish or greyish patches often caused due to hormonal changes.
- Sun spots: small, dark spots appearing on the skin because of long-term sun exposure.
- Liver spots: Small, dark spots appearing on the skin because of long-term sun exposure.
- Hypopigmentation: Lighter patches that occur due to decreased melanin production.
Blemishes And Pigmentation Difference: Treatment Tips For Each
Now that you know a whole lot of blemish pigmentation differences in terms of meaning, causes, and types, it’s time to delve deeper into how to treat both effectively:
A Step-by-Step Guide on Best Treatment For Blemishes on Face
Here are the four skincare suggestions to help you treat blemishes on your face effectively:
1. Cleanse two times a day
Regardless of your skin type or problems, cleansing is a must-have starting step of any skincare routine. Wash your face with a simple face wash every morning and night to help remove extra oil and dirt from your skin.
2. Use retinol
Retinol, as a vitamin A derivative, can also help prevent skin imperfections. Try a mild retinol-infused serum if you’re using it for the first time, which will smooth, brighten, and refine skin while absorbing fast.
3. Prioritize Hydration
Apply a non -comedogenic moisturiser to strike a perfect balance between hydration and your skin problems like blemishes or spots. Those with oilier or acne-prone skin should apply a lighter, water-based moisturiser.
4. Adopt safe sun practices
Age spots and blemishes are examples of skin issues that may get more pronounced when exposed to the sun. Thus, it is important to protect your skin from harmful sun radiation. For this, apply a broad-spectrum SPF sunscreen, use sun protective clothing, and avoid direct sunlight whenever possible.
A Step-by-Step Guide on Effective Pigmentation Treatment
The right pigmentation treatment, knowing the steps on how to apply it correctly, and other skincare practices will help you achieve clear and glowing skin. Here are the key pointers on treating pigmentation effectively:
Cleansing and prepping of skin
To let every drop of pigmentation cream work its magic, start with a gentle cleanser to let skin absorb products better. Gently pat dry skin. Wait a minute or two before applying treatments.
Application steps for maximum efficacy
Now, apply a thin, even layer of your pigmentation treatment cream, focusing on the affected parts. Avoid rubbing, use gentle patting motions, and always follow the instructions printed on the specific product.
Frequency and use duration
Pigmentation treatments require patience. You need to use most products consistently for 6-12 weeks before you will see noticeable improvements.
Blend with skincare routine
Timing is important. Most pigmentation treatments function best at night when your skin goes into repair mode. Apply pigmentation products after cleansing but before moisturiser, followed by SPF in the morning. Your regular skincare routine should complement, not compete with, your pigmentation treatment.
Are Pigmentation And Dark Spots The Same?
Before going into the details of similar skin problems like pigmentation and dark spots, in terms of the differences. It is important to know that, similar to pigmentation and blemishes, terms like pigmentation vs dark spots are often used interchangeably in skincare. But both are different skincare phenomena.
Pigmentation is the natural coloration of the skin, while dark spots usually refer to localized areas of hyperpigmentation. While pigmentation affects the colour of the skin, hair, and at times, even the eyes. Dark spots are usually visible in various parts of the body, such as hands, shoulders, and face.
Difference Between Dark Spots and Pigmentation

The key difference between pigmentation and dark spots is that pigmentation can affect larger areas and include various colors (light, dark, red, or grey). In contrast, dark spots are typically smaller, well-defined patches, often caused by factors such as sun exposure, acne scars, or injury.
Pigmentation
- Definition: A general term for a change in skin color due to melanin overproduction.
- Appearance: Can appear as larger, more diffuse areas of darkened or discolored skin.
- Color: Can range from light to dark, red, or grey.
- Causes: Broader range, including hormonal changes, sun damage, and underlying medical conditions like thyroid disorders.
- Treatment: Often requires more comprehensive treatments like systemic therapies, topical treatments, and procedures like chemical peels or laser treatments.
Dark spots
- Definition: A specific, more localized form of hyperpigmentation.
- Appearance: Small, isolated, well-defined spots.
- Color: Typically brown, black, or greyish.
- Causes: Commonly caused by specific events such as sun damage, acne scars, and other skin injuries.
- Treatment: Can often be treated with targeted, topical skincare products or minor procedures.
Common Myths And Misconceptions About Blemishes And Pigmentation
Many myths about reducing blemishes and pigmentation abound to complicate the treatment options. Here are the 5 myths and facts of each of these skin problems.
Debunking Top 5 Myths About Pigmentation
| Myth | Fact |
| Only those with acne get pigmentation | No, pigmentation may occur due to hormones, injuries, or sun exposure, not simply acne. |
| Only fair-skinned people get pigmentation | No, pigmentation can affect people of all skin tones. In fact, darker skin tones are more prone to it. |
| Scrubbing can remove pigmentation | Over-exfoliation may damage the skin barrier, causing increased inflammation and triggering more melanin production, which may make pigmentation worse. |
| You don’t need sunscreen indoors to prevent pigmentation | Blue light from screens and indirect sunlight may also worsen pigmentation. So, apply sunscreen even when indoors. |
| All pigmentation is the same. | Not all pigmentation is the same. There are many types of pigmentation, and each needs a specific approach to treatment. |
Debunking Top 5 Myths About Blemishes
| Myth | Fact |
| Scrubbing the face removes blemishes | Harsh exfoliation may irritate your skin and stimulate more inflammation or scarring. |
| Blemishes imply your skin is unhealthy | Skin naturally changes. Blemishes are not an indicator of poor health. |
| Washing your face frequently will clear up blemishes | No, frequent washing of the face will not help clear blemishes. Overwashing can strip away your skin’s natural moisture barrier. |
| Popping blemishes may make them go away faster. | The temptation to pop a blemish or pimple is not a safe practice and may even cause permanent scarring. |
| Makeup causes blemishes. | Not all makeup causes blemishes. The development of blemishes or acne from makeup varies as the type of products used and how they are applied and removed. |
Ayurvedic Remedies for Pigmentation and Blemishes
Treating Blemishes with Ayurveda
- Neem: Helps reduce acne and prevents future breakouts.
- Turmeric: Lightens acne scars and maintains an even skin tone.
- Sandalwood: Reduces inflammation and redness associated with blemishes.
Treating Pigmentation with Ayurveda
- Aloe vera: Treats dark spots and soothes the skin.
- Licorice: Inhibits production of melanin.
- Saffron: It helps preserve a youthful glow.
Conclusion
Hopefully, the blog on pigmentation and blemishes has provided extensive coverage on the difference between blemishes and pigmentation. And knowing the difference will help you choose the right treatment. Moreover, it will allow it to treat your skin with more care, less frustration, and a greater amount of self-respect.
FAQs
What is the difference between pigmentation and blemishes?
The key difference is that pigmentation relates to the color of the skin itself, while blemishes are visible flaws on the skin’s surface that may or may not include discoloration.
Can pigmentation and blemishes be removed permanently?
Mild pigmentation and blemishes can often be lightened or removed with consistent skincare, sun protection, and treatments like chemical peels or laser therapy. However, maintenance is key to preventing recurrence.
How can I treat pigmentation and blemishes naturally at home?
Home remedies like applying aloe vera gel, lemon juice (with caution), turmeric paste, potato juice, or rose water can help lighten dark spots. Always do a patch test before trying any remedy to avoid irritation.
Which skincare ingredients help fade pigmentation and blemishes?
Look for products containing ingredients such as vitamin C, niacinamide, licorice extract, kojic acid, alpha arbutin, glycolic acid, and retinol — all of which help brighten skin and reduce discoloration.
How long does it take to see results from pigmentation treatments?
Results vary depending on the severity of pigmentation and the treatment used. Typically, visible improvement can be seen within 4–8 weeks with consistent skincare and sun protection.
Can sunscreen help prevent pigmentation and blemishes?
Absolutely! Sunscreen is one of the most effective ways to prevent pigmentation. Daily use of a broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher protects skin from UV rays that trigger melanin production.
Are pigmentation and blemishes related to acne?
Yes. After acne heals, it often leaves behind dark spots or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), which are forms of blemishes. Proper acne treatment and sun protection can reduce their occurrence.
What professional treatments are effective for pigmentation and blemishes?
Dermatologists may recommend chemical peels, microdermabrasion, laser therapy, or intense pulsed light (IPL) treatments to fade pigmentation and even out skin tone effectively.
Can diet and lifestyle affect pigmentation and blemishes?
Yes, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants (vitamin C, E, and zinc), adequate hydration, and reduced stress levels promotes healthy skin and prevents excessive pigmentation and blemishes.
Can stress cause pigmentation and blemishes?
Yes, chronic stress can indirectly cause pigmentation and blemishes. Stress hormones like cortisol can trigger inflammation and hormonal imbalances, leading to acne breakouts and post-inflammatory dark spots.



